Indigenous Governance Database
cultural match
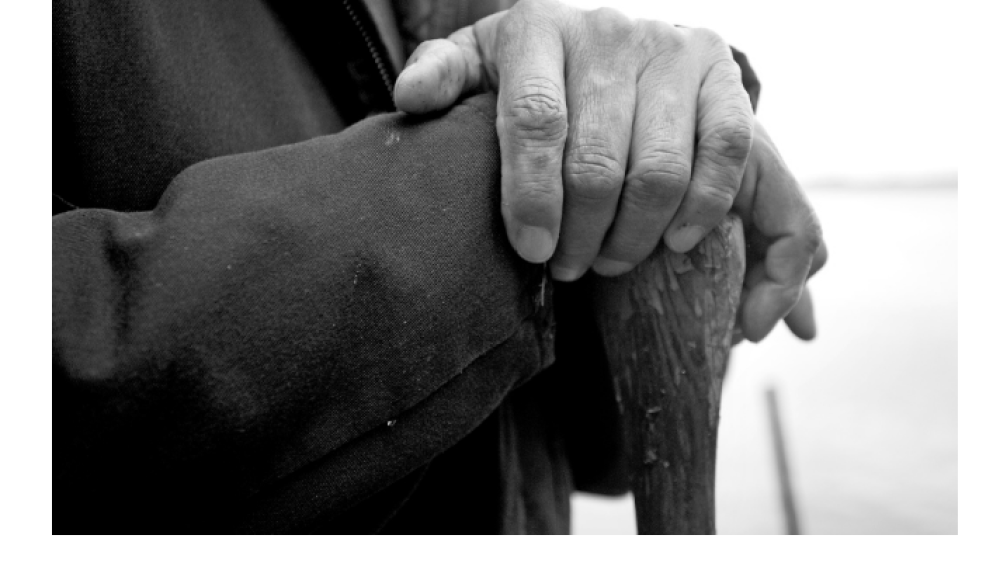

'We are getting stronger'
An economic, political and cultural renaissance is underway throughout Indian Country in the United States. It’s been going on for nearly a quarter-century. Whereas in the 1980s, economic growth on Indian reservations lagged far behind the rate of the U.S. economy, through the booming 1990s and the…
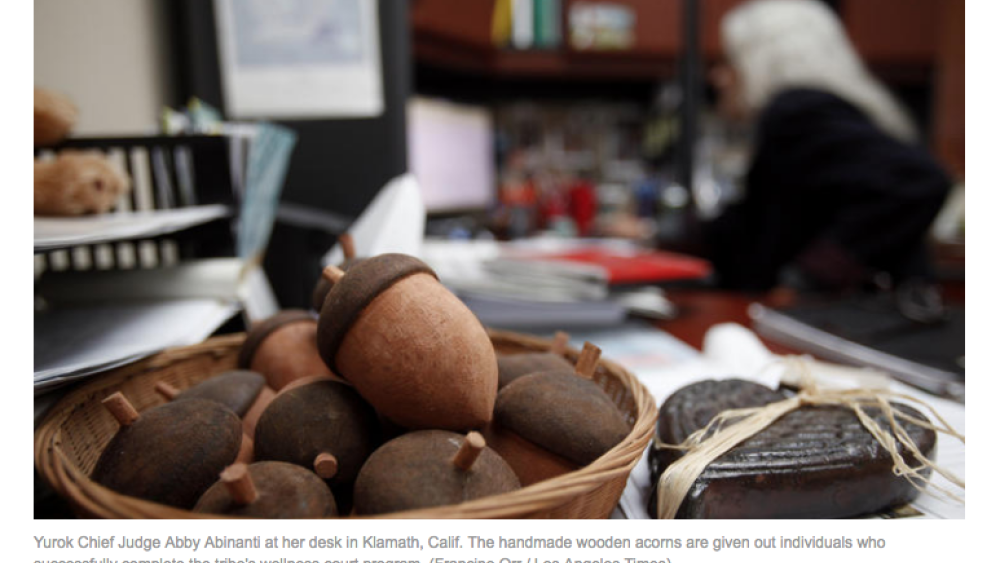

Yurok tribe's wellness court heals with tradition
Lauren Alvarado states it simply: “Meth is everywhere in Indian country.” Like many here, she first tried methamphetamine at age 12. Legal trouble came at 13 with an arrest for public intoxication. In the years that followed, she relied on charm and manipulation to get by, letting her grandmother…

White Earth Nation Adopts New Constitution
In a historic vote, on November 19, 2013, the White Earth Nation in northwestern Minnesota became the first member of the Minnesota Chippewa Tribe (MCT) to adopt a new constitution. Of the 3,492 ballots counted, the vote was 2,780 in favor and 712 opposed, a 79 percent approval. Since the ballots…

American Indian tribe OKs same-sex marriage, lets gay couple wed
The head of an American Indian tribe in Michigan signed a law approving same-sex marriage on Friday, joining at least two other tribes nationwide in doing so, then immediately wed a gay couple who had been together for 30 years but never thought they would see this day come...
The Harvard Project on American Indian Economic Development and its Application to Canadian Aboriginal Business
This lecture is part of a course Stephen Cornell is teaching in Simon Fraser University's Executive MBA in Aboriginal Business and Leadership program. A panel of three joined Dr. Cornell in a discussion about the building of First Nation economies and the role citizen entrepreneurship can play in…

SEEDocs - Owe'neh Bupingeh Preservation Plan and Rehabilitation Project
Re-creating a more vital Pueblo center and reinvigorating cultural heritage traditions through the rehabilitation of the historic Pueblo core was this project's focus. The Pueblo core is the spiritual, social and cultural center of the Pueblo. Community members were trained in traditional building…

Nisga'a First Nation Circle of Governance
People of the Nisga'a Nation discuss custom and tradition before the Indian Act. They tell how they made the move back to traditional ways through strategic planning and abandoned oppressive ways of the Indian Act.

These Are My People...
This documentary short is the first film made by an all-Aboriginal film crew, training under the NFB's Challenge for Change Program. It was shot at Akwesasne (St. Regis Reserve). Two spokesmen explain historical and other aspects of Longhouse religion, culture, and government and reflect on the…

Ktunaxa Nation: Building from their Vision
This video, produced by the National Centre for First Nations Governance, offers a history behind the vision or mission statement of the Ktunaxa Nation in British Columbia.

Developing a First Nation Constitution
Chiefs, Administrators and Advisors discuss the importance of constitutions and the work involved in developing their own nation's constitution.

NCFNG: Governance and Cultural Match
Taken from a 2008 event hosted by the National Centre for First Nations Governance, this video looks at the question: "How does a First Nation match governance with their culture and traditions?"
Joseph P. Kalt: The Nation-Building Renaissance in Indian Country: Keys to Success
Harvard Project on American Indian Economic Development Co-Director Joseph P. Kalt presents on the Native nation-building renaissance taking root across in Indian Country, and shares some stories of success.
Stephen Cornell: Two Approaches to Building Strong Native Nations
Harvard Project on American Indian Economic Development Co-Director Stephen Cornell presents the research findings of the Harvard Project and the Native Nations Institute, specifically the two general approaches that Native nations pursue in an effort to achieve sustainable community and economic…

Aboriginal Youth Entrepreneurship: Success Factors and Challenges
Aboriginal people (First Nations, Métis and Inuit) and their communities in the north face many obstacles and challenges. There are, however, tremendous opportunities to promote and enhance Aboriginal participation in the economy. Aboriginal youth entrepreneurs are key to building a healthy…

Minding Our Own Businesses: how to create support in First Nations communities for Aboriginal Business
The purpose of the project was to investigate what other First Nations have done to support their small business operators, and to create a process to look at what could be done in your community...

Strategies for Creating Offender Reentry Programs in Indian Country
Weed and Seed, a community-based strategy sponsored by DOJ, is an innovative, comprehensive, multi-agency approach to law enforcement, crime prevention, and community revitalization. The strategy aims to prevent, control, and reduce violent crime, drug abuse, and gang activity in designated high-…

Oneida Tribe of Indians of Wisconsin: Food Sovereignty, Safe Water, and Tribal Law
An example of a Native American community working to achieve food sovereignty not only with physical nutrients but also with social elements is the Oneida Tribe of Indians of Wisconsin. This article analyzes the strengths of the Oneida Tribe's approach to preserving water quality and fishing…

First Nation Constitutions
A constitution is a solid foundation for First Nations to move ahead in self-government and in nation-building activities. Your constitution will be specific to your community. It should address your community's sense of itself, how you are governed, how the membership has input into governance,…

Best Practices Case Study (Rule of Law): Nisga'a Nation
Nisga'a Nation, comprised of four communities; New Aiyansh, Gitwinksihlkw, Laxgalt'sap, and Gingolx, is located in northwestern B.C. In the 1890s, Nisga'a hereditary chiefs and matriarchs formed the Nisga'a Land Committee and began to aggressively pursue self-government and title to their lands.…

Best Practices Case Study (Expansion of Jurisdiction): Tsawwassen First Nation
Tsawwassen First Nation (TFN) is located in the Metro-Vancouver area of British Columbia. In 2007, following 14 years of negotiations, TFN signed a treaty with Canada and B.C. It was the first treaty reached under the BC Treaty Commission (BCTC) process and the first urban treaty. The Effective…
Pagination
- First page
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- …
- Last page
